Understanding Partial Knee Replacements: A Comprehensive Guide
Benton Franklins Orthopedic Associates is the Tri-Cities area leader in joint replacement and revisions with award-winning fellowship-trained providers in Trauma and Total Joint Replacement.
If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to feel pain while you are sitting or lying down. If nonsurgical treatments like medications, injections, and walking supports are no longer helpful, you may want to consider total knee replacement surgery.
Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help you resume normal activities.
Below you'll find valuable information on total knee replacement. For more information please contact us by scheduling a consultation at 509-586-2828
What is Arthritis?
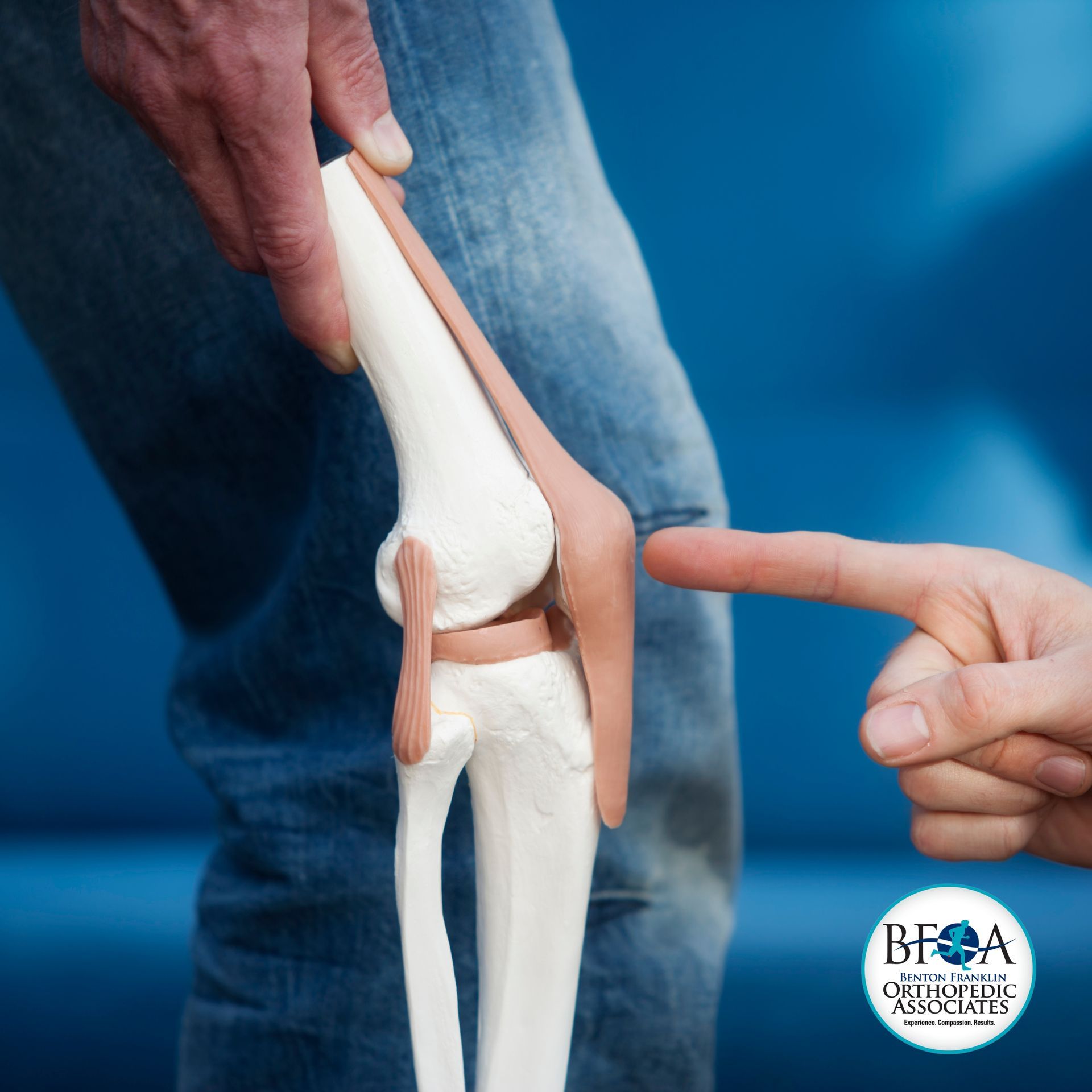
The knee is composed of the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and patella (kneecap). The meniscus, a soft cartilage between the femur and tibia, acts as a cushion and helps absorb shock during movement. Arthritis, which is the inflammation of the joints, along with injuries or other joint diseases, can damage this protective cartilage layer, leading to severe pain and difficulty in performing daily activities. Osteoarthritis is a common type of arthritis. If non-surgical treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery.
Causes of Osteoarthritis:
The exact cause of osteoarthritis is unknown, but several factors are commonly associated with its onset, including:
- Injury or trauma to the joint
- Fractures at the knee joint
- Increased body weight
- Repetitive overuse
- Joint infection
- Inflammation of the joint
- Connective tissue disorders
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis:
Your doctor will diagnose osteoarthritis based on your medical history, a physical examination, and X-rays. X-rays typically reveal a narrowing of the joint space in an arthritic knee.
Indications for Total Knee Replacement:
Total knee replacement surgery is often recommended for severe osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of knee arthritis, where the joint cartilage gradually wears away, often affecting older individuals. In a healthy joint, articular cartilage allows for smooth movement. However, in an arthritic knee, the cartilage becomes thinner or may be completely absent. Additionally, the bones around the joint edges may thicken and form bony "spurs," causing pain and restricting the joint's range of motion.
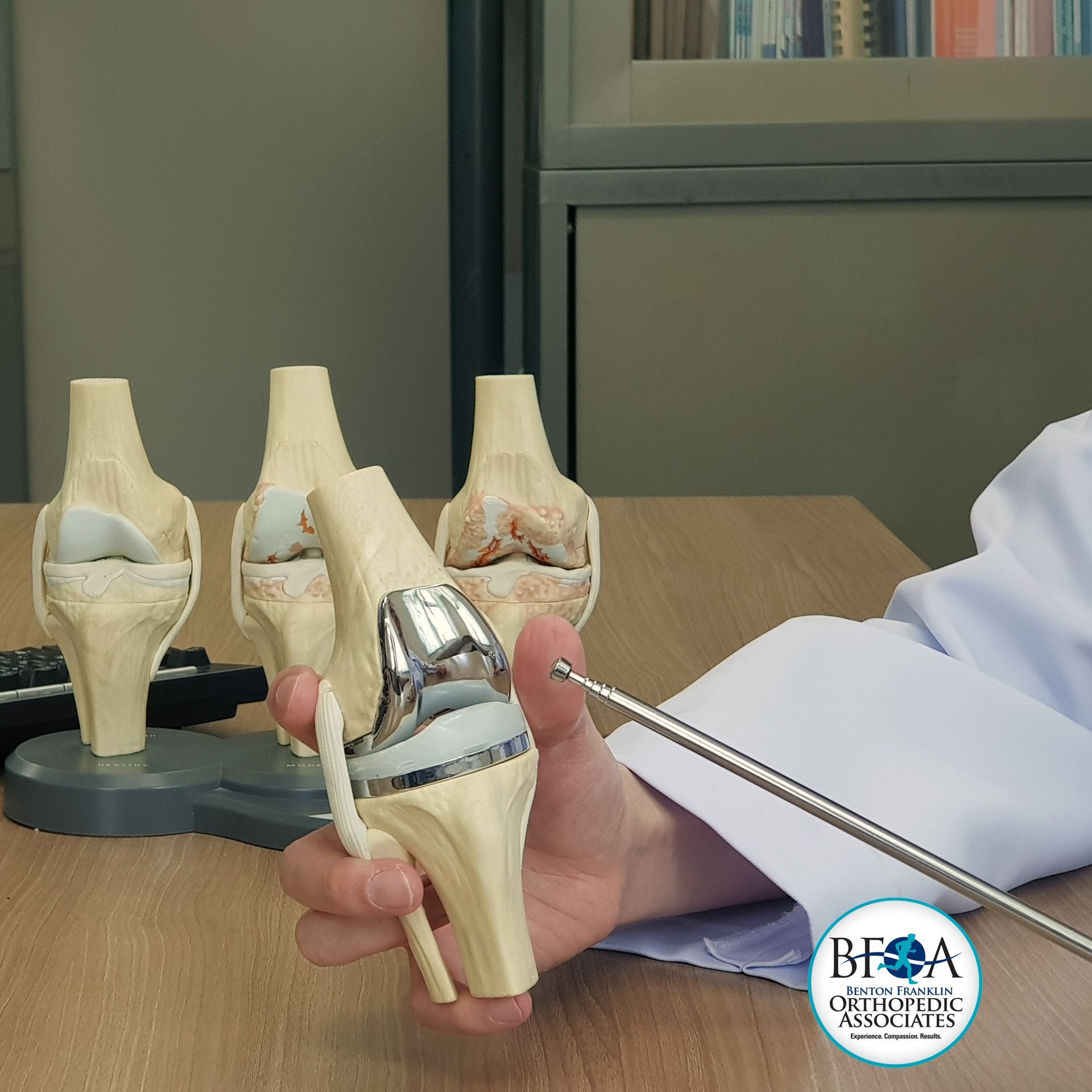
What is a Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure where only the damaged part of the knee joint is replaced with a prosthetic. This is different from a total knee replacement, which involves replacing the entire knee joint. Partial knee replacements are typically recommended for patients with osteoarthritis confined to a single compartment of the knee.
Benefits of Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacements offer several advantages over total knee replacements, including:
- Less Invasive Surgery: The procedure involves smaller incisions and less disruption to the surrounding tissues.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often experience quicker recovery times and can return to normal activities sooner.
- Preservation of Natural Knee Movement: Since only part of the knee is replaced, the natural movement and function of the knee are better preserved.
- Reduced Pain: Patients typically report less postoperative pain compared to total knee replacement.
Conditions Treated by Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacements are primarily used to treat osteoarthritis, but they can also be effective for other conditions affecting the knee, such as:
- Medial Compartment Arthritis: The most common type of arthritis treated with partial knee replacement.
- Lateral Compartment Arthritis: Less common but still treatable with this procedure.
- Patellofemoral Compartment Arthritis: Arthritis affecting the area under the kneecap.
- Trauma from Accidents: Injuries from car accidents or other traumatic events can damage the cartilage or ligaments in the knee, making partial knee replacement a viable option for recovery.
- Overuse of the Joint: Repetitive stress and overuse can lead to joint degeneration, making partial knee replacement an effective treatment option.
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery from a partial knee replacement typically involves:
- Initial Recovery: Most patients can start moving and walking with assistance shortly after surgery.
- Full Recovery: It usually takes around six weeks for patients to fully recover and return to their normal activities.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help improve mobility and strengthen the knee.
Is Partial Knee Replacement Right for You?
Not everyone with knee arthritis, trauma, or overuse injuries is a candidate for partial knee replacement. Ideal candidates typically have:
- Arthritis confined to one compartment of the knee
- Functional ligaments
- Good range of motion
- Overall knee stability
Partial knee replacement can also serve as a stepping stone to delay a total knee replacement. By addressing the damaged area early, patients can potentially extend the life of their natural knee and delay the need for a more extensive total knee replacement.
If you're experiencing knee pain and stiffness that hasn't improved with nonsurgical treatments, or if you've suffered a knee injury from an accident or overuse, partial knee replacement might be an option worth considering.
Consult with the experts at Benton Franklin Orthopedic Associates to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition. For more information or to schedule an appointment contact Benton Franklin Orthopedic Associates at (509) 586-2828.