Total Knee Replacement in Kennewick, WA
Benton Franklins Orthopedic Associates is the Tri-Cities area leader in joint replacement and revisions with award-winning fellowship-trained providers in Trauma and Total Joint Replacement.
If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to feel pain while you are sitting or lying down. If nonsurgical treatments like medications, injections, and walking supports are no longer helpful, you may want to consider total knee replacement surgery.
Joint replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help you resume normal activities.
Below you'll find valuable information on total knee replacement. For more information please contact us by scheduling a consultation at 509-586-2828
What is Arthritis?
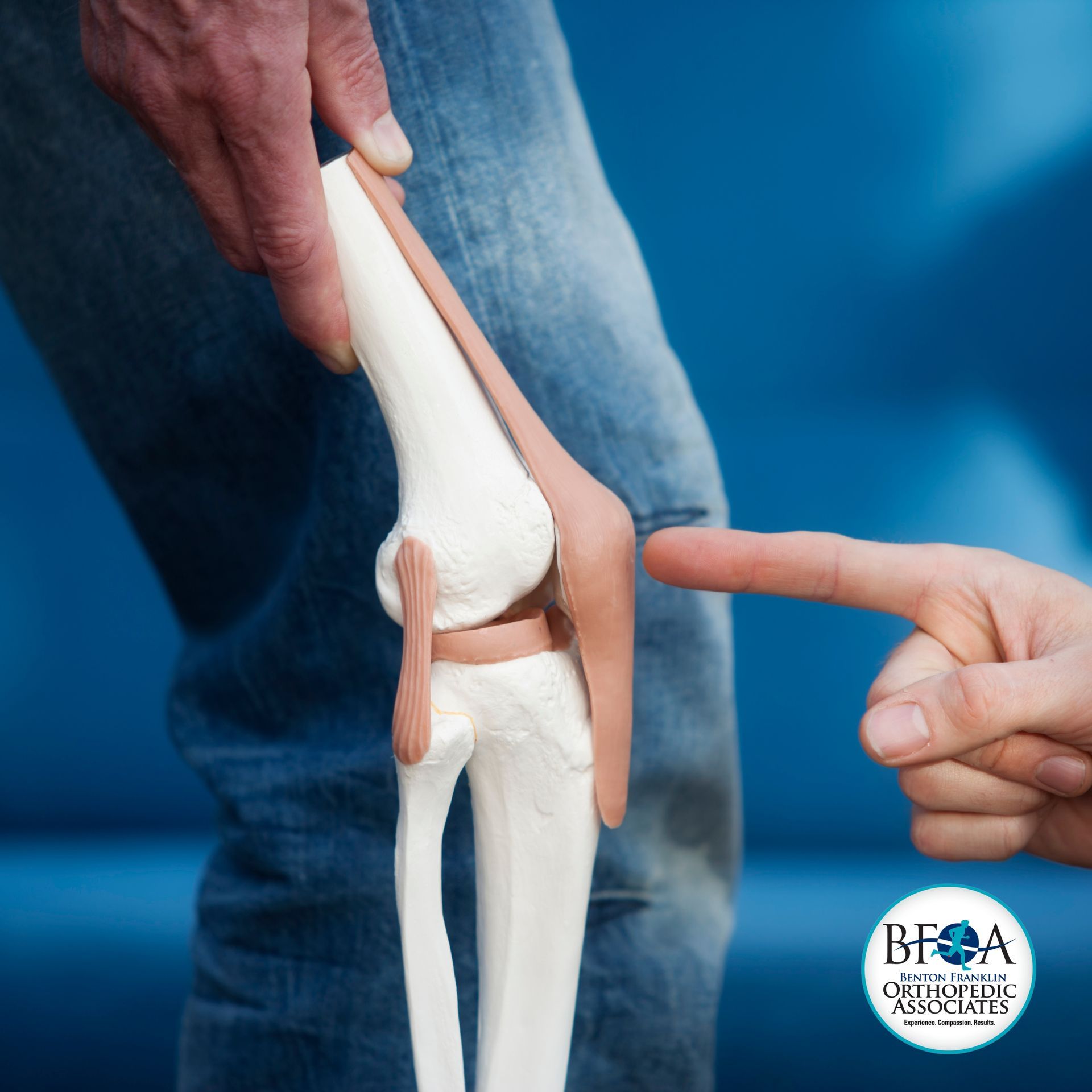
The knee is composed of the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and patella (kneecap). The meniscus, a soft cartilage between the femur and tibia, acts as a cushion and helps absorb shock during movement. Arthritis, which is the inflammation of the joints, along with injuries or other joint diseases, can damage this protective cartilage layer, leading to severe pain and difficulty in performing daily activities. Osteoarthritis is a common type of arthritis. If non-surgical treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery.
Causes of Osteoarthritis:
The exact cause of osteoarthritis is unknown, but several factors are commonly associated with its onset, including:
- Injury or trauma to the joint
- Fractures at the knee joint
- Increased body weight
- Repetitive overuse
- Joint infection
- Inflammation of the joint
- Connective tissue disorders
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis:
Your doctor will diagnose osteoarthritis based on your medical history, a physical examination, and X-rays. X-rays typically reveal a narrowing of the joint space in an arthritic knee.
Indications for Total Knee Replacement:
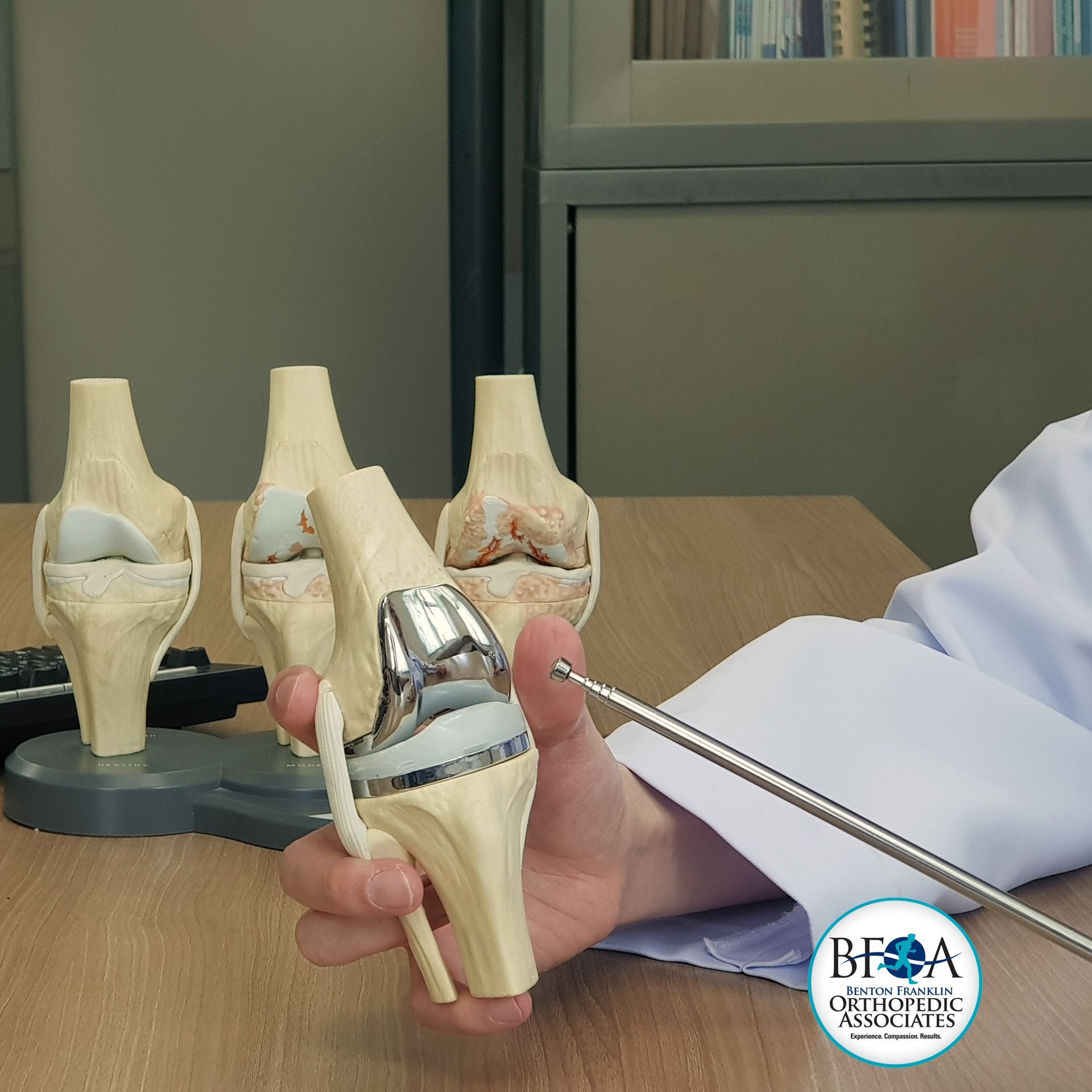
Total knee replacement surgery is often recommended for severe osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of knee arthritis, where the joint cartilage gradually wears away, often affecting older individuals. In a healthy joint, articular cartilage allows for smooth movement. However, in an arthritic knee, the cartilage becomes thinner or may be completely absent. Additionally, the bones around the joint edges may thicken and form bony "spurs," causing pain and restricting the joint's range of motion.
Total Joint Replacement:
- Minimally Invasive Joint Replacement
Total Knee Replacement Procedure
The goal of total knee replacement surgery is to relieve pain and restore the alignment and function of your knee.
The surgery is performed under spinal or general anesthesia. Your surgeon will make an incision in the skin over the affected knee to expose the knee joint. Then, the damaged portions of the femur bone are cut at appropriate angles using specialized jigs. The femoral component is attached to the end of the femur with or without bone cement.
The surgeon then cuts or shaves the damaged area of the tibia (shinbone) and the cartilage. This removes the deformed part of the bone and any bony growths, creating a smooth surface on which the implants can be attached. Next, the tibial component is secured to the end of the bone with bone cement or screws.
Your surgeon will place a plastic piece called an articular surface between the implants to provide a smooth gliding surface for movement. This plastic insert will support the body’s weight and allow the femur to move over the tibia, similar to the original meniscus cartilage.
The femur and tibia with the new components are then put together to form the new knee joint.
To ensure the patella (kneecap) glides smoothly over the new artificial knee, its rear surface is also prepared to receive a plastic component.
With all the new components in place, the knee joint is tested through its range of motion. The entire joint is then irrigated and cleaned with a sterile solution. The incision is carefully closed, drains are inserted, and a sterile dressing is placed over the incision.
Postoperative Care Following Total Knee Replacement
Rehabilitation begins immediately following the surgery. A physical therapist will teach you specific exercises to strengthen your leg and restore knee movement. Knee immobilizers are used to stabilize the knee. You will be able to walk with crutches or a walker.
It is very important you attend all home or onsite physical therapy.
Your physical therapist will also provide you with a home exercise program to strengthen thigh and calf muscles.
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience pain from a traumatic injury you should seek immediate medical attention. You should see a doctor if your pain is accompanied by deformed joints, you are unable to walk or move your leg or cannot bear weight on your injured leg. When low to moderate levels of pain persists longer than a week and self care remedies including rest, over the counter pain relievers, ice or heat do not improve your condition you should contact your doctor.
For more information or to schedule an appointment contact Benton Franklin Orthopedic Associates at (509) 586-2828.